- +86-755-23012705
- Building 3, Jinfeng Industrial Park, Fuyong Street, Baoan District, Shenzhen ,China
- [email protected]
High-frequency board refers to the special electromagnetic frequency circuit board, used in high frequency (greater than 300 MHZ frequency or wavelength is less than 1 meter) and microwave (greater than 3 GHZ frequency or wavelength is less than 0.1 meters) in the field of PCB, is on the microwave base copper clad using common rigid circuit board manufacturing method of a part of the process or the use of special processing methods and the production of circuit boards. In general, a high-frequency board can be defined as a circuit board with a frequency of more than 1GHz.
With the rapid development of science and technology, more and more equipment designs are applied in microwave frequency band (> 1GHZ) and even above the millimeter wave field (30GHZ), which also means that the frequency is getting higher and higher, and the requirements on the base material of circuit board are also getting higher and higher. For example, the substrate material needs to have excellent electrical performance, good chemical stability, with the increase of the power signal frequency on the substrate loss requirements are very small, so the importance of high-frequency plate protrudes out.
2.1 Mobile communication products
2.2 Power amplifier, low noise amplifier, etc
2.3 Passive devices such as power dividers, couplers, diplexers, filters, etc
2.4 Automobile anti-collision system, satellite system, radio system and other fields.
High frequency of electronic equipment is the development trend.
3.1 Powder ceramic filled thermosetting material
Manufacturer:
Rogers 4350B/4003C
25N/25FR for Arlon
Taconic’s TLG series
Processing method:
Similar to epoxy/glass woven fabric (FR4), but the plates are brittle and easily broken. The life of drill tip and gongs is reduced by 20% for drilling and routing.
3.2 PTFE(Teflon) material
A: The manufacturer
Rogers RO3000 series, RT series, TMM series
Arlon’s AD/AR series, IsoClad series, CuClad series
Taconic RF series, TLX series, TLY series
F4B, F4BM, F4BK and TP-2 of Taixing microwave
B: Processing method
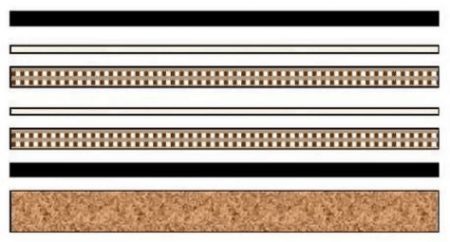
High-frequency plate routing plate lamination method
After the routing, the board edge burrs need to be carefully scraped by hand, to prevent damage to the substrate and copper surface, and then use the appropriate size of sulfur-free paper separation, and visual detection, to reduce burrs, the key is the gongs process to the effect of good.
4.1. PTFE plate processing process of NPTH
Material opening – drilling – dry film – inspection – etching – corrosion inspection – welding resistance – character – spray tin – molding – test – final inspection – packaging – shipment
4.2. PTFE plate processing process of PTH
Material opening – drilling – hole treatment (plasma treatment or sodium naphthene activation treatment)- immersed copper – plate electricity – dry film – inspection – graphic electricity – etching – welding resistance – character – spray tin – forming – test – final inspection – packaging – shipment






XPCB Limited is a premium PCB & PCBA manufacturer based in China.
We specialize in multilayer flexible circuits, rigid-flex PCB, HDI PCB, and Rogers PCB.
Quick-turn PCB prototyping is our specialty. Demanding project is our advantage.
Tel : +86-136-3163-3671
Fax : +86-755-2301 2705
Email : [email protected]
© 2024 - XPCB Limited All Right Reserve
